ADDENDUM
The report you are about to read is one of six “exploratory studies” commissioned by the UN Environment TEEB Office, funded by the Global Alliance for the Future of Food, and carried out by the National Commission for the Knowledge and Use of Biodiversity (CONABIO) in Mexico, to begin building an evidence base to feed into the wider initiative on TEEB for Agriculture & Food (TEEBAgriFood). The original purpose of these studies was to assess the impacts and dependencies arising from particular agricultural sectors and systems.
Since then, the TEEBAgriFood study has designed and developed an Evaluation Framework that seeks to be universal and comprehensive in coverage, both in terms of all economic, environmental and social dimensions as well as looking across the value chain (production, processing and distribution, and waste).
The purpose of this document is to contextualize this study and its coverage within the larger mandate of TEEBAgriFood and its Evaluation Framework. This includes a brief description of the development of the Framework, a detailed look at what is and is not covered by the scope of this study, and some recommendations for future research that may help support the goals of the TEEBAgriFood project.
Introduction to TEEBAgriFood
The economic environment in which farmers and agricultural policymakers operate today is distorted by significant externalities, both negative and positive. Indeed, most of the largest impacts on the health of humans, ecosystems, agricultural lands, waters, and seas arising from various different types of agricultural and food systems are economically invisible and do not get the attention they deserve from decision-makers. There is therefore a need to evaluate all significant externalities of eco-agri-food systems, to better inform decision-makers in governments, businesses and farms. Furthermore, there is a need to evaluate the eco-agri-food systems complex as a whole, and not as a set of silos.
TEEBAgriFood will seek to develop a comprehensive and universally applicable evaluation framework, which will allow to assess agricultural systems, practices, products and policy scenarios against a comprehensive range of impacts and dependencies along the food value chain.
As one of the first steps of this process, a number of exploratory studies were commissioned in early 2014 in order to assess some of the major “externalities-heavy” agricultural sectors, including: agroforestry, inland fisheries, livestock, palm oil, rice and, later, maize. Their objective was “to assess the visible and invisible values of biodiversity and ecosystems to all types of agricultural systems (inputs) and evaluate the scale, range and degree of both positive and negative externalities of specific agri-business sectors on ecosystems, health and livelihoods (outputs).”
More recently, however, the development of an Evaluation Framework has resulted in a broadening of value-chain coverage from production only (i.e. within ‘farm gate’) to include processing/distribution and consumption. Additionally, certain data limitations and challenges in terms of time forced more limited results than anticipated from these studies.
On the one hand, these studies should not be treated as full applications of the Framework. On the other hand, their findings (although partial) do offer some extremely important insights into the impacts and dependencies of agriculture and food systems that should be considered a fundamental starting point for further research.
The sections below illustrate which “cells” of the Framework have and have not been assessed, as well as whether this was done using quantitative, qualitative or monetary techniques. It is important to mention that this note only focuses on coverage, whereas the report itself (accessible at the end of this document) takes a deep dive into each of the issues as well as presenting important policy, business and research recommendations.
Coverage of the TEEBAgrifood Evaluation Framework in this study
The purpose of this section is to assess how well the Maize exploratory study aligns with the Framework, and how comprehensively this study has identified and valued the impacts and dependencies of this particular agricultural sector on ecosystems and human wellbeing across all stages of the food value chain.
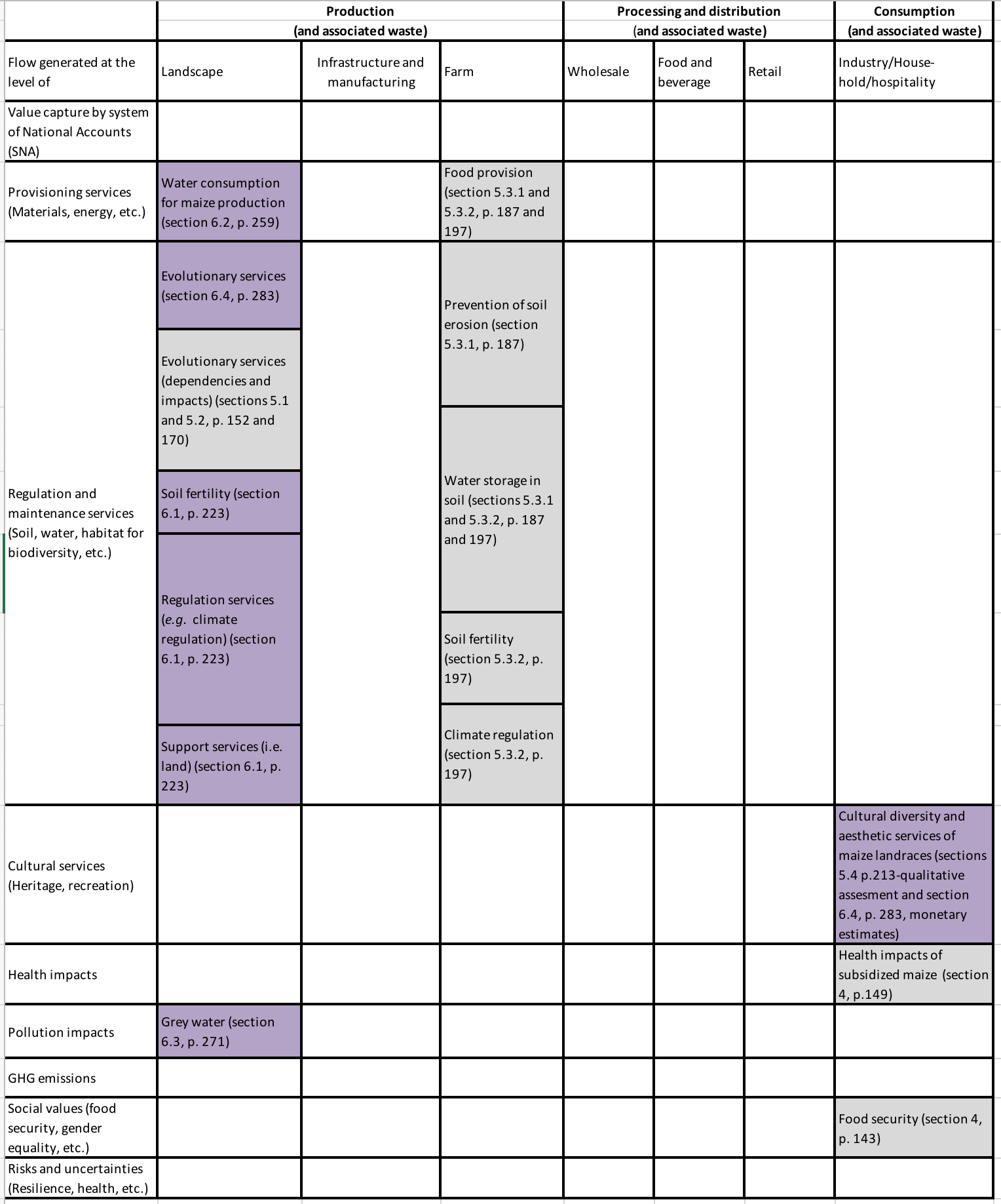
Annex I presents the TEEBAgriFood Evaluation Framework. The left-hand column (or y-axis) of the framework identifies the visible and invisible impacts and dependencies that can be influenced, both positively and negatively, by different agriculture and food systems. The top row (or x-axis) distinguishes three main stages in the food value chain throughout which these flows should be assessed: production, processing/distribution, and consumption (plus the waste generated at each stage). Each stage is then further sub-divided into categories, e.g. changes to landscape and manufacturing of inputs within the production phase.
The process of filling the cells within this framework depends on the extent to which this study evaluated impacts and dependencies across the food value chain. First, it was determined whether a cell has been sufficiently covered in the study; empty cells indicate non-existent or inadequate coverage. Second, the contents within cells describe specifically which flows were covered by the study. Finally, the difference in shading corresponds to the type of method (monetary, quantitative or qualitative) used by the study for evaluating that flow.
This study on Maize focused predominantly on the production phase. Within this stage, it concentrated on the landscape, using publicly available data on maize production at the global, national and subnational scales. However, some ecosystem services at the farm-gate scale were also addressed through the revision of specific case studies. The set of databases used for the calculation of the monetary estimates generated in this study are made available for any further analyses.
The study further addressed the evolutionary services provided by maize systems high in genetic diversity thus highlighting the relevance of these seldom assessed ecosystem service.
The impacts of infrastructure and manufacturing during the production phase, as well as all aspects related to the processing/distribution phase were not included in this study. Regarding the consumption phase, the study extensively discussed the cultural services provided by native maize varieties and provided some monetary estimates about their value for smallholder peasants in Mexico.
Further research
As explained in the previous section, further research would be needed to fill the evaluation gaps identified in this study.
For the production phase, this study identified the need to count with management data at lower spatial scales to improve the quantification and estimation of the dependencies of maize systems on diverse ecosystem services.
At the landscape scale there is a need to quantitatively evaluate how and to what extent agro-biodiverse maize systems ensure access to food security/sovereignty and health benefits to rural populations with difficult access to local and national markets. Additionally, information regarding the resilience of different maize systems to climate change, in order to assess its impact on the food security of different populations worldwide may also prove vital.
Quantitative and monetary estimates about evolutionary services provided by crop intraspecific diversity to present and future maize production (under climate change scenarios) remain unaccounted for, and are therefore required.
Further research is needed in maize taxonomy, genetics, agronomy, agricultural practices, uses and their relationship with ecosystem services (both dependencies and impacts), as well as socioeconomic and cultural factors.
With regards to the consumption phase, manufactured products (like high-fructose corn syrup-HFCS) derived from maize have been linked to liver and other metabolic diseases that potentially strain public health systems. There is a need to generate monetary estimates about these costs, especially in countries with elevated consumption of HFCS.
Further research will, therefore, bring about a more comprehensive and holistic assessment of the impacts and dependencies of the Maize sector on ecosystems and human wellbeing, that can better inform policy and practice aimed to achieve sustainability and social value for the sector.
Annex I - TEEBAgriFood Evaluation Framework
- Full Study Maize - Final Report
- Annex 1 - Spatial analysis and mapping
- Annex 2 - Production function
- Annex 3 - Water databases
- Annex 4 - Valuation of ecosystem services
- Annex 5 - Participants Directory
- Slideshow presentation
- Evolutionary and food supply implications of ongoing maize domestication by Mexican campesinos
- La gran contribución de los campesinos maiceros a México y al mundo
- Beyond subsistence: the aggregate contribution of campesinos to the supply and conservation of native maize across Mexico (Access requires subscription)
Citation
CONABIO (2017) Ecosystems and agro-biodiversity across small and large-scale maize production systems. TEEB Agriculture & Food, UNEP, Geneva.